Home / Science / Baby galaxy cluster defies cosmic rules
Baby galaxy cluster defies cosmic rules
5 Jan
Summary
- Galaxy cluster found 1.4 billion years post-Big Bang.
- Cluster's gas is five times hotter than expected.
- Three supermassive black holes may cause the heat.
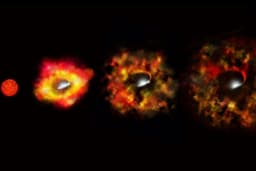
Scientists have identified a nascent galaxy cluster, SPT2349-56, that existed just 1.4 billion years after the Big Bang. Astonishingly, this cluster is five times hotter than current astrophysical models predict for such an early stage of the universe's development. The unexpected high temperatures challenge established theories about cosmic evolution and the formation of galaxy clusters.
Researchers utilized the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) to observe this ancient object, which spans over 500,000 light-years. The intracluster medium, the superheated gas between galaxies, is reaching extreme temperatures, far exceeding expectations for an immature cluster. This finding suggests that early cosmic processes might have been more vigorous than previously believed.
While the exact cause remains under investigation, a leading theory posits that three supermassive black holes residing within the cluster are generating immense energy. These black holes, known for their rapid growth in the early universe, could be actively heating the surrounding gas and shaping the cluster's environment, offering new insights into the universe's formative epochs.