Home / Health / Gas Offers Hope Against Superbug Pneumonia
Gas Offers Hope Against Superbug Pneumonia
11 Feb
Summary
- Inhaled nitric oxide shows promise against resistant pneumonia.
- High doses of gas reduced superbugs in a pig ICU model.
- Safety trials in humans show low methemoglobin levels.
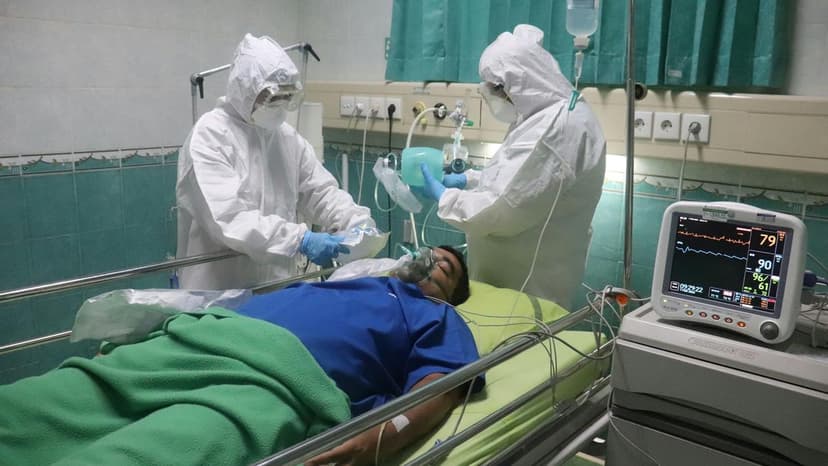
In intensive care units, drug-resistant pneumonia, especially from Pseudomonas aeruginosa, poses a significant challenge due to limited treatment options.
Researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital have investigated the use of inhaled nitric oxide, a gas naturally produced by the body and used clinically at low doses, at much higher concentrations.
A study published in Science Translational Medicine utilized a large-animal ICU model involving pigs infected with multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa. One group received high-dose inhaled nitric oxide (300 ppm) for short periods, while the control group received standard care.