Home / Health / Deadly Nipah Virus: What You Need to Know
Deadly Nipah Virus: What You Need to Know
28 Jan
Summary
- Nipah virus has a high fatality rate of 40%-75%.
- It primarily spreads from fruit bats to humans through contaminated fruit.
- No approved vaccines or treatments are currently available.
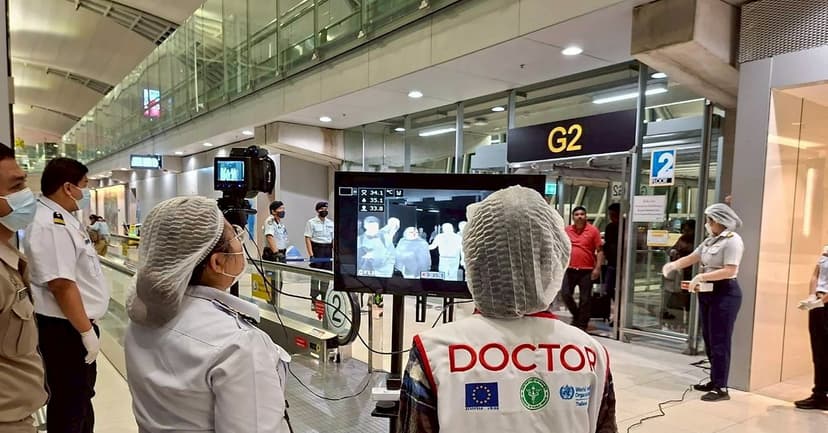

Recent Nipah virus cases in India have prompted heightened airport screening measures in Thailand and Malaysia. This rare viral infection, with a significant fatality rate of 40% to 75%, is primarily transmitted from fruit bats to humans. The most common transmission route involves consuming fruit or raw date palm juice contaminated by infected bats.
First identified in Malaysia in 1999, Nipah has since caused small, contained outbreaks, predominantly in Bangladesh and sporadically in India. While human-to-human transmission can occur through close contact, it is not easily facilitated. Scientists note that Nipah has not shown signs of becoming more transmissible globally, and airport screening might be limited due to its long incubation period.
There are currently no approved vaccines or treatments for Nipah. However, research is ongoing, with candidate vaccines utilizing similar technology to COVID-19 vaccines entering phase II testing in Bangladesh. This effort aims to develop critical medical tools against emerging disease threats.