Home / Health / HPV Vaccine Halts Cervical Cancer Growth
HPV Vaccine Halts Cervical Cancer Growth
25 Nov
Summary
- HPV vaccines significantly reduce cervical cancer risk, especially when given pre-exposure.
- Two global reviews confirm the vaccine's effectiveness against HPV-related conditions.
- Common side effects are mild, with serious adverse events being rare.
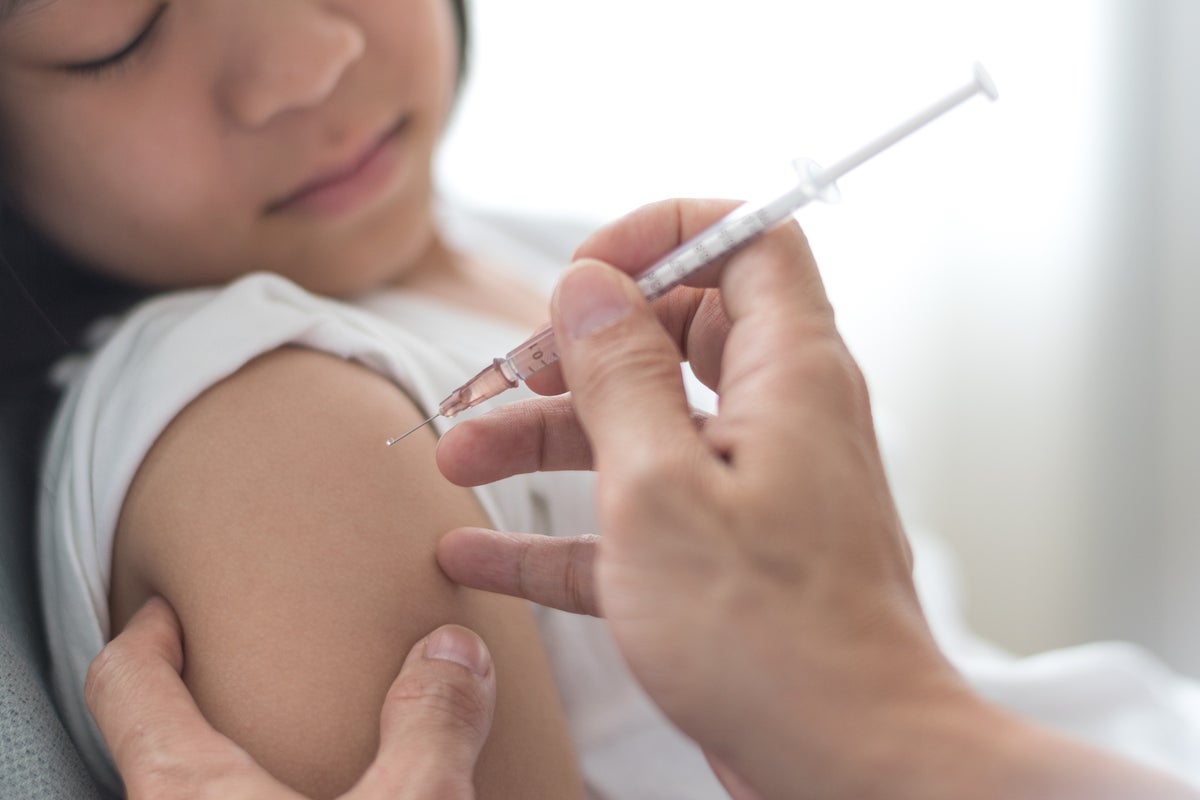
Recent comprehensive reviews of global data confirm that HPV vaccines are exceptionally effective in preventing cervical cancer. These vaccines, particularly when administered to adolescents before exposure to the virus, demonstrably reduce the incidence of precancerous cervical changes and associated conditions like anogenital warts. The findings, which analyzed data from millions across numerous studies, offer clear evidence of the vaccine's protective benefits.
Cervical cancer, a significant global health issue causing over 300,000 deaths annually, can be largely averted through vaccination. The reviews highlight that vaccines such as Cervarix, Gardasil, and Gardasil-9 are crucial tools in this fight. While cancers can take years to develop, the evidence clearly points to a substantial reduction in related precancerous conditions, providing strong indicators of future cancer prevention.
Commonly reported side effects from the HPV vaccine are mild, typically limited to pain or swelling at the injection site, with serious adverse events being extremely rare. Health experts advocate for vaccinating both boys and girls before the age of 16 to maximize protection against HPV-related cancers, emphasizing that this proactive measure is key to saving lives and reducing cancer burdens worldwide.