Home / Environment / Waste to Energy: Powering the Future or Polluting It?
Waste to Energy: Powering the Future or Polluting It?
2 Feb
Summary
- Waste-to-energy converts non-recyclable waste into usable fuel.
- Facilities can reduce waste volume by 90%, extending landfill life.
- India operates 21 WtE plants and 133 biogas facilities.
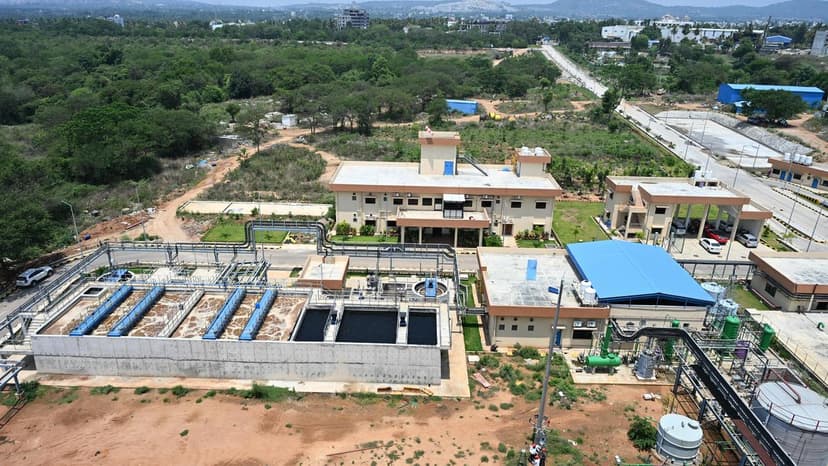

Waste-to-energy (WtE) offers a method to convert non-recyclable waste materials into usable energy sources like heat or electricity. Common techniques include incineration, gasification, and anaerobic digestion. These facilities play a crucial role in waste management by reducing waste volume by approximately 90%, thereby extending the operational life of landfills and diminishing the need for new ones.
India is a significant player in this sector, currently operating at least 21 WtE plants and 133 biogas facilities. These operations are guided by the Solid Waste Management Rules 2026, which promote waste segregation and the use of refuse-derived fuel. This focus aims to alleviate the pressure on existing landfill sites across the nation.
While WtE presents benefits such as substantial waste reduction and potential methane emission avoidance from landfills, environmental concerns persist. The burning of waste can release carbon dioxide and pollutants, though modern facilities often employ advanced filtration systems. Debates continue regarding WtE's influence on recycling and composting efforts.