Home / Technology / Microscopic Robots Now Swim: A Medical Revolution?
Microscopic Robots Now Swim: A Medical Revolution?
29 Jan
Summary
- Researchers created the smallest programmable robots ever built.
- These robots move using electrokinetics without any moving parts.
- Production costs could drop below one cent per robot.
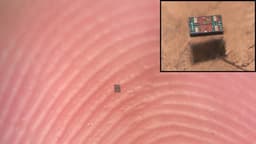
Researchers have overcome a long-standing physics barrier by developing the world's smallest fully programmable robots, each measuring about 200 by 300 by 50 micrometers. These microscopic machines are capable of autonomous movement, a feat previously confined to science fiction.
Instead of traditional propellers or legs, the robots utilize electrokinetics. They generate a small electrical field that manipulates surrounding ions to propel themselves through fluid. This design ensures extreme durability and ease of handling, even with delicate laboratory equipment.
Powered by minuscule solar cells generating only 75 nanowatts, these robots feature ultra-low voltage circuits and a highly compressed instruction set. They possess the ability to sense their environment, store data, and autonomously decide on their next action, mimicking natural communication through programmed wiggles.