Home / Science / Ancient Rome's Roads: More Vast Than Imagined
Ancient Rome's Roads: More Vast Than Imagined
9 Dec
Summary
- Roman road network estimated length increased to 187,460 miles.
- New digital atlas uses historical and satellite data.
- The road system aided Roman expansion and cultural spread.
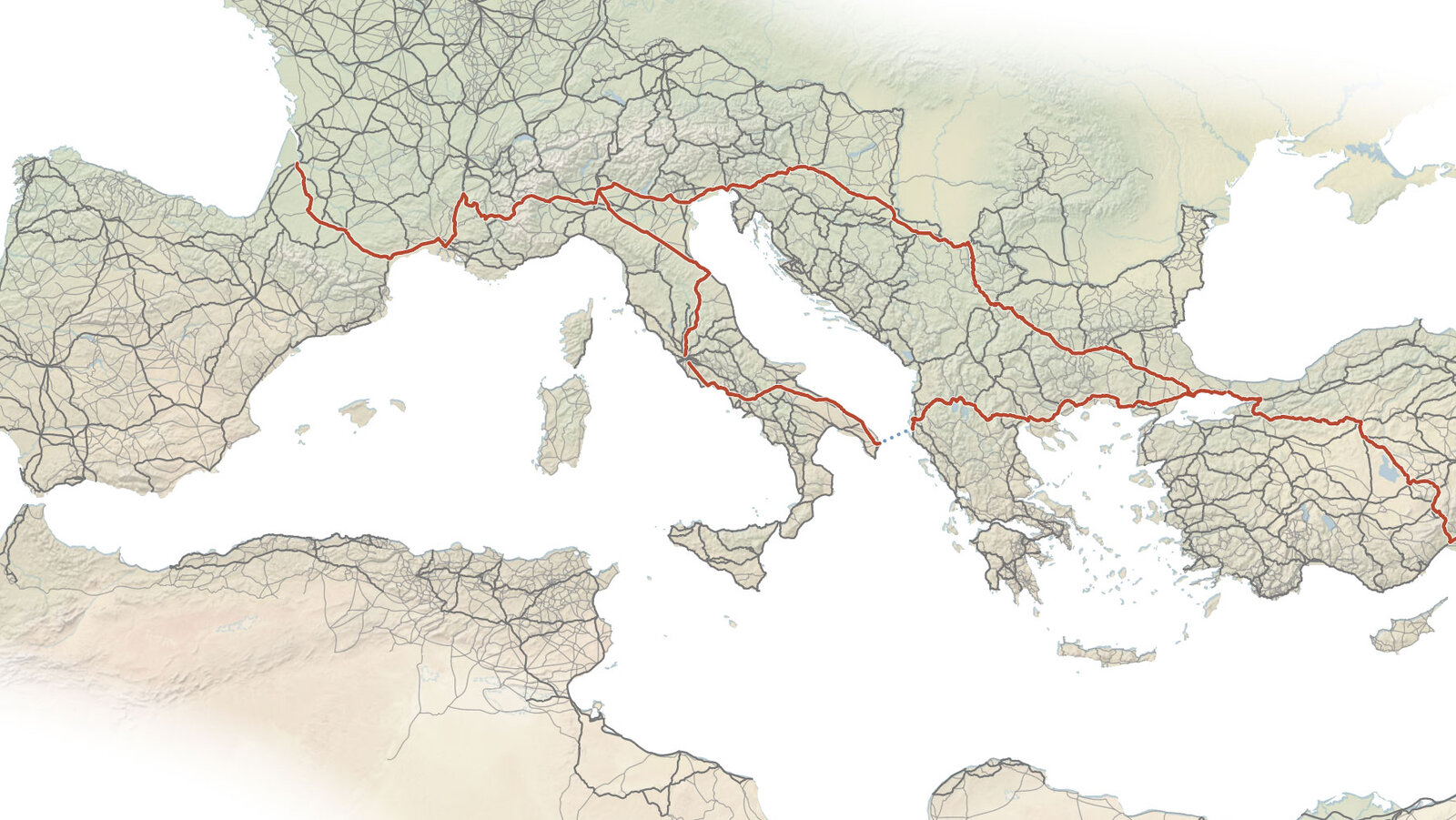
An extensive digital atlas named Itiner-e has unveiled that the Roman Empire's road network was significantly larger than previously estimated, reaching an impressive 187,460 miles. This comprehensive study integrated historical records with modern satellite and topographic data to model travel times across ancient routes. The findings challenge earlier, narrower definitions of Roman roads, which primarily focused on major engineered thoroughfares.
The research broadened the scope to include all walkable paths, employing a terrain-following mapping technique that substantially increased the mapped networks in areas like North Africa and Greece. Researchers utilized aerial analysis and subtle land changes to identify lost byways, acknowledging that less than 3 percent of Roman road locations are precisely confirmed.
This revised understanding of the Roman transportation system highlights its crucial role in troop movement, trade, and the spread of ideas, including early Christianity. The pilgrimage route described in the "Itinerarium Burdigalense" exemplifies the network's importance in connecting regions and facilitating cultural and religious exchange across the vast empire.




