Home / Science / Same-Sex Behavior in Primates Linked to Survival
Same-Sex Behavior in Primates Linked to Survival
2 Feb
Summary
- Primates show same-sex behaviors in harsh environments.
- Homosexuality may forge bonds crucial for group survival.
- SSBs are more common in species facing environmental challenges.
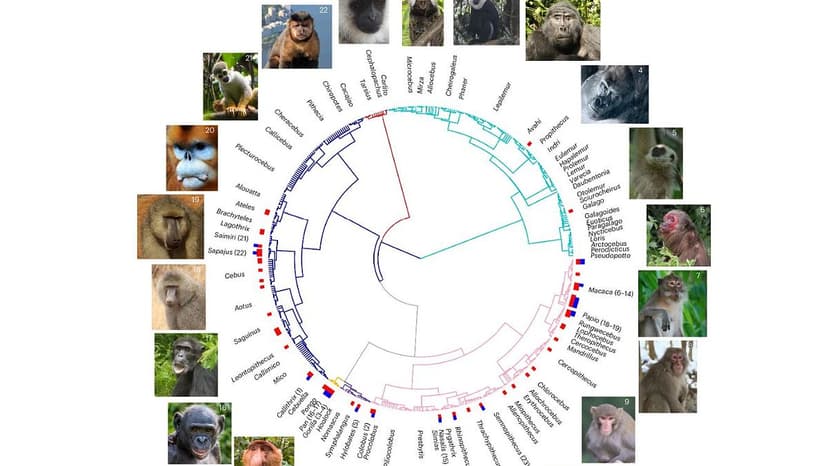
A recent study from Imperial College London proposes that same-sex behaviors (SSBs) in primates may serve as an evolutionary survival strategy. Researchers observed that SSBs are more prevalent in primate species facing difficult environmental conditions, such as drier habitats, scarcer resources, or increased predator presence. These challenging circumstances appear to favor the development of strong social bonds within groups.
The study analyzed data from 491 non-human primate species, identifying SSBs in 59. The findings suggest that homosexuality might help strengthen social cohesion, enabling groups to better withstand environmental pressures. For instance, tight-knit groups with established trust can respond more effectively to threats like predators.
While previous research indicated a possible genetic component to SSBs in some primates, this new analysis emphasizes the significant role of environmental and social factors. The experts suggest that SSBs have likely evolved multiple times across primate lineages, partly as a mechanism for navigating complex social and ecological systems. Further research is planned to explore these links directly.



