Home / Science / Life's Ancient Whispers: New Tech Finds 3.3B-Year-Old Signs
Life's Ancient Whispers: New Tech Finds 3.3B-Year-Old Signs
18 Nov, 2025
Summary
- New method detects oldest life signs in 3.3 billion-year-old rocks.
- Photosynthesis evidence found in 2.5 billion-year-old South African rocks.
- Machine learning distinguishes biological from non-biological molecules.
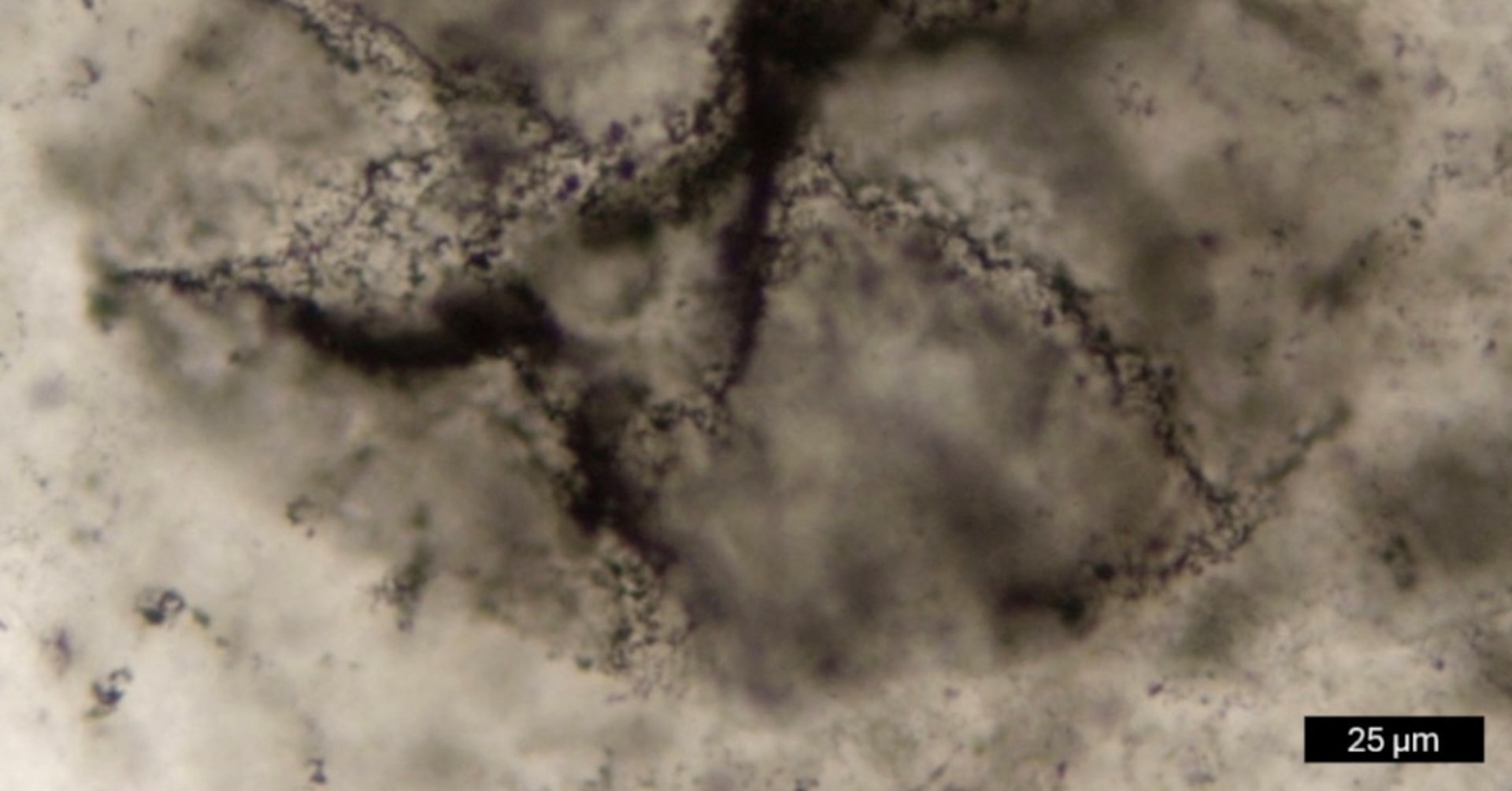
A groundbreaking method employing machine learning has allowed scientists to detect some of the oldest signs of life on Earth. This new technique analyzes chemical fingerprints within ancient rocks, achieving over 90% accuracy in distinguishing between biological and non-biological organic molecules. This approach has revealed evidence of microbial life in rocks approximately 3.3 billion years old.
Furthermore, the research identified molecular traces of oxygen-producing photosynthesis in rocks around 2.5 billion years old. This discovery suggests that this vital process was occurring much earlier than previously documented by similar evidence. The ability to discern these subtle chemical patterns is a significant advancement in paleontology.