Home / Health / US Preterm Birth Crisis Worsens
US Preterm Birth Crisis Worsens
19 Nov, 2025
Summary
- Preterm birth rates increased in 21 states year-over-year.
- Southern states show significantly higher preterm birth rates.
- Lifestyle, socioeconomic factors, and healthcare access are key drivers.
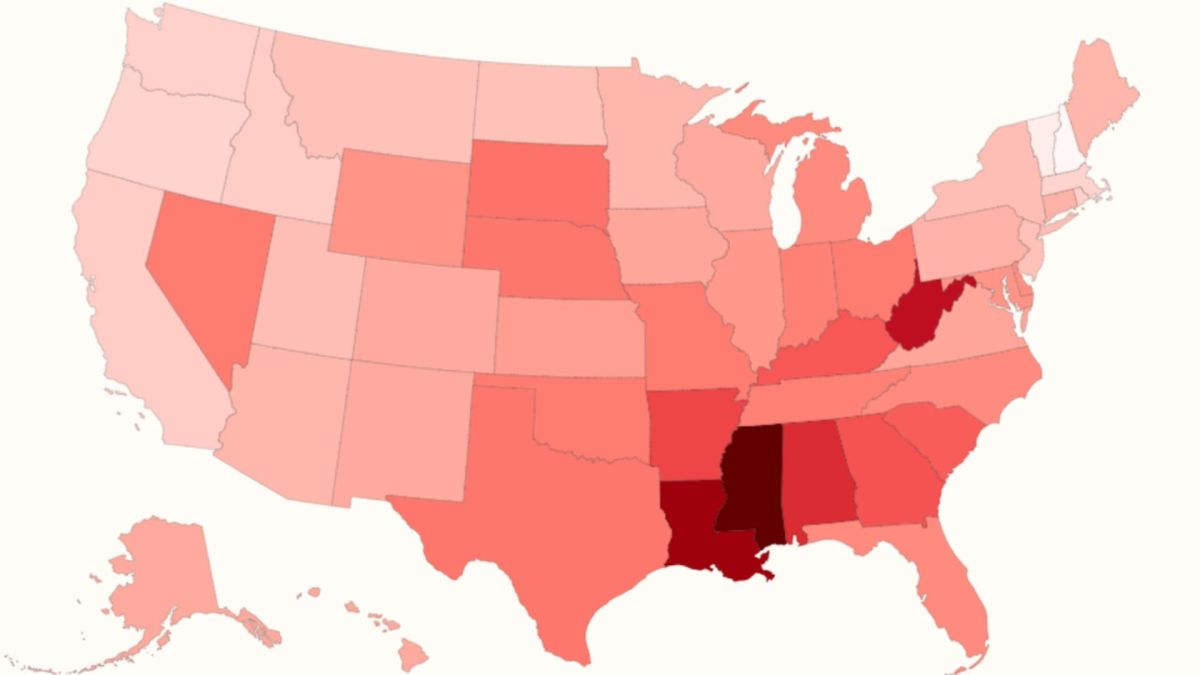
The United States is facing a worsening preterm birth crisis, with 21 states reporting higher rates this past year compared to the previous one. Preterm birth, defined as birth before 37 weeks of gestation, is a critical indicator of broader population health and is increasingly linked to conditions like obesity and hypertension. The national average preterm birth rate stands at 10.4 percent for 2024.
Southern states disproportionately bear the brunt of this crisis, with several recording rates of 11.5 percent or higher. Mississippi, Louisiana, and West Virginia are among those with the highest rates. Experts attribute these disparities to social and environmental disadvantages, reduced access to quality healthcare, and challenges in maintaining healthier lifestyles in these regions.
Conversely, states like New Hampshire have significantly lower preterm birth rates, attributed to better overall population health, higher life expectancy, and favorable living conditions including low poverty levels and access to healthy resources. Improving these rates nationally requires a focus on preventative health, education, economic opportunities, and robust public health support before and during pregnancy.




