Home / Health / Tongue Cancer: Beyond Tobacco's Shadow
Tongue Cancer: Beyond Tobacco's Shadow
3 Feb
Summary
- Heavy alcohol use significantly raises tongue cancer risk, even without tobacco.
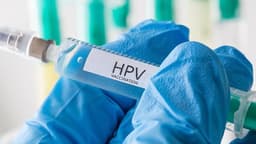
- HPV infection causes approximately 20% of oral cancers, including tongue cancer.
- Poor oral hygiene, diet, genetics, age, and gender also contribute to risk.

Tongue cancer, a form of oral cancer, can develop due to various factors beyond tobacco use. While smoking and chewing tobacco are primary causes, alcohol consumption is a significant risk factor. Heavy drinking can increase the vulnerability of oral cells to cancerous changes, with the risk escalating when combined with tobacco. Approximately 20% of oral cancers are now attributed to Human Papillomavirus (HPV) infections, with younger individuals increasingly diagnosed with HPV-related tongue cancer.
Poor oral hygiene, characterized by chronic irritation from untreated dental issues, can also contribute to tongue cancer. A diet lacking in fruits and vegetables may reduce protective antioxidants, while processed and high-fat foods might increase risk. Genetic predisposition and family history are also considered, as is age, with those over 40 being more susceptible, though younger cases are rising. Men are statistically more likely to develop tongue cancer than women.