Home / Health / Drinking Just 2-3 Glasses of Wine a Week Increases Deadly Liver Disease Risk
Drinking Just 2-3 Glasses of Wine a Week Increases Deadly Liver Disease Risk
11 Nov
Summary
- Consuming more than 2 drinks/week for women, 3 drinks/week for men increases liver disease risk
- Being overweight/obese is the most important risk factor for metabolic-associated fatty liver disease
- First-line treatment includes diet, exercise, and avoiding alcohol
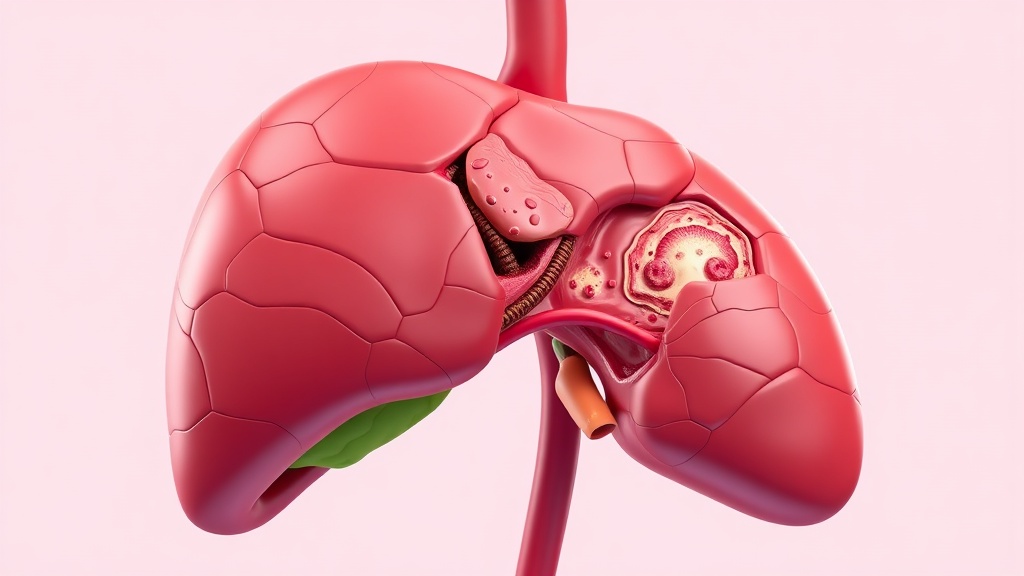
According to a comprehensive study published in JAMA in November 2025, consuming more than 2 standard alcoholic drinks per week for women and 3 drinks per week for men can dramatically increase the risk of developing a deadly liver disease known as metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD).
The research, led by a team from the Medical University of Innsbruck, Austria, reviewed over 100 studies on MASLD, previously called non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. The analysis found that being overweight or obese is the single most important risk factor for this potentially life-threatening illness, which is estimated to affect up to 40% of people globally.
Other key risk factors include high blood pressure, low "good" cholesterol, elevated blood sugar, a sedentary lifestyle, smoking, and excessive sugar intake. Genetics and hormonal changes like menopause can also increase the likelihood of developing MASLD. Experts have emphasized that the first line of treatment involves behavioral modifications such as a weight-reducing diet, regular exercise, and complete avoidance of alcohol.



