Home / Health / Tiny Genetic Flaw Causes 'Baby Alzheimer's'
Tiny Genetic Flaw Causes 'Baby Alzheimer's'
6 Dec, 2025
Summary
- Genetic defect causes brain cells to 'rust' and die.
- Discovery offers hope for treating childhood and adult dementias.
- Researchers slowed cellular rusting in lab experiments.
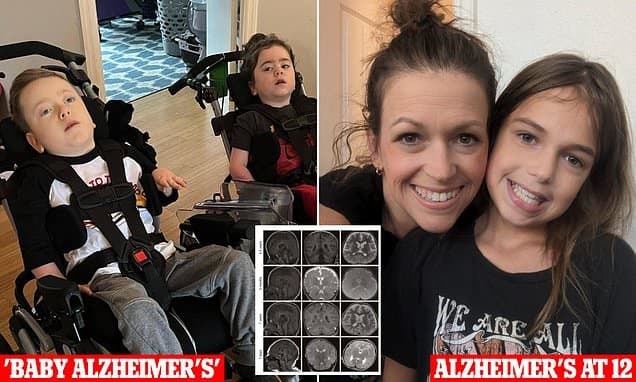
Researchers have pinpointed a crucial genetic defect responsible for a form of childhood dementia, often referred to as 'baby Alzheimer's.' This flaw disrupts the GPX4 enzyme, which normally prevents a cell-death process characterized by 'rusting.' When defective, neurons corrode from within and die, a mechanism potentially involved in adult neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer's disease.
The international research team's findings not only illuminate the cause of these rare and devastating childhood disorders but also mark a significant step towards potential treatments. In laboratory settings, scientists have demonstrated the ability to mitigate this cellular 'rusting,' offering a beacon of hope for affected families and the broader field of dementia research.
This breakthrough shifts focus from traditional protein deposit theories to the initial damage of cell membranes. By understanding this fundamental process, scientists are paving the way for novel therapeutic strategies that could impact a wide spectrum of brain diseases, from rare childhood conditions to more common adult dementias.