Home / Health / AI Diagnoses Rare Diseases, Offers Life-Saving Advice
AI Diagnoses Rare Diseases, Offers Life-Saving Advice
30 Jan
Summary
- ChatGPT is increasingly used by people for medical advice.
- AI can identify rare diseases doctors might overlook.
- AI offers potential benefits but carries significant risks.
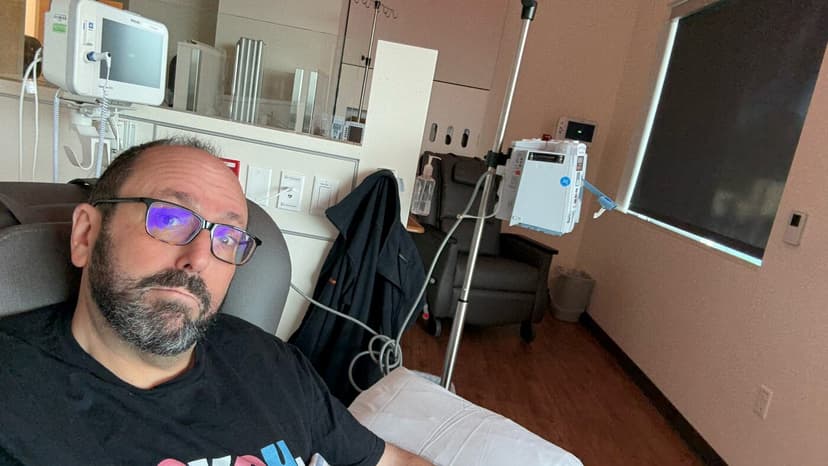
Artificial intelligence, particularly tools like ChatGPT, is rapidly becoming a significant resource for health information and preliminary diagnostics. Millions now consult these platforms weekly, with some users sharing instances where AI provided crucial advice that led to timely medical intervention for rare conditions.
Unlike human doctors who often follow a 'horses, not zebras' diagnostic approach due to time constraints, AI can dedicate extensive time to patient inquiries. This allows AI to explore less common diagnoses and analyze extensive medical knowledge beyond typical generalized understanding.
Patients are leveraging AI for daily well-being, managing chronic conditions, and translating complex medical test results. Some even use it to make understanding their diseases more memorable, often by requesting information in a specific persona, thus shifting their doctor appointments towards action-planning sessions.
However, the integration of AI in healthcare is not without considerable risks. As a consumer product, ChatGPT Health is not subject to the same stringent health privacy regulations as clinical systems. Lawsuits have emerged alleging psychological harm, including suicide-related claims, highlighting mental health concerns.
Medical professionals emphasize that AI is a supplement, not a replacement, for doctors. Without clinical oversight, there's a substantial risk of misdiagnosis, misleading advice, or misunderstanding, as seen in cases advising ivermectin for cancer or sodium bromide for salt intake reduction.
Despite these hazards, many experts are optimistic about AI's future in healthcare, foreseeing its benefits to eventually surpass the dangers. Studies indicate AI's diagnostic reasoning capabilities are competitive with humans, and tools like AI Scribe and OpenEvidence are already improving doctors' efficiency and patient interaction.
As AI continues its rapid integration into healthcare systems, its adoption is expected to become seamless for future generations. While concerns about AI's broader societal impact persist, its potential to support a struggling healthcare system in the United States is viewed by some as essential.




