Home / Environment / Kilauea Erupts: Lava Soars 1500 Feet High
Kilauea Erupts: Lava Soars 1500 Feet High
13 Jan
Summary
- Incandescent lava is being hurled over 1,500 feet into the air.
- Volcanic smog (vog) poses respiratory risks to nearby areas.
- Eruptions typically last a day but can release significant gases.
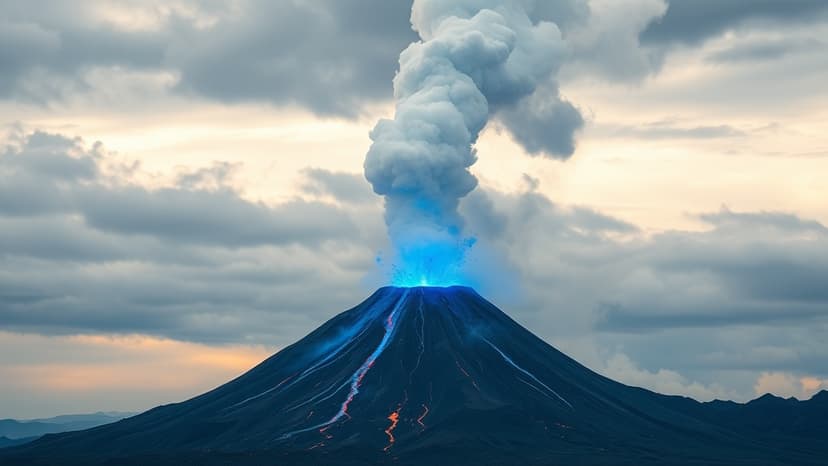

Hawaii's Kilauea volcano has been actively erupting since December 2024, showcasing a dramatic fountain of lava. Volcanologists report that incandescent molten rock is being ejected more than 1,500 feet into the atmosphere. Accompanying this spectacle are plumes of smoke and gases rising as high as 20,000 feet, contributing to air quality concerns.
The US Geological Survey notes that these eruptions, though often lasting around a day, can release up to 100,000 tonnes of sulfur dioxide. This gas transforms into volcanic smog, known as vog, which can lead to respiratory problems. Additionally, sharp strands of volcanic glass, termed 'Pele's hair,' are being dispersed, posing a risk of skin and eye irritation.
Despite its powerful display, the current eruption poses no immediate threat to human settlements, as the caldera has been closed to the public for nearly two decades. Kilauea, one of six active volcanoes in the Hawaiian Islands, is renowned for its frequent and impressive eruptions, drawing tourists eager to witness its fiery activity.